No, I'm not putting this in /c/electoralism , for reasons found in the third paragraph
Most people know there's first-past-the-post and there's ranked-choice. But I've recently learned there's a much longer list than that, and they all have pros and cons.
Somecomrades would say 🙄yeah bourgeois elections who cares🙄 but that is wrong: the mathematics applies to all voting. It's the engineering side of the question: "If we have a bunch of people, maybe a hundred, maybe a million, how do we decide what the collective will is in the fairest way?" The name of the field is social choice theory because a social group is trying to make a choice.
You: oh bourgeois elections are a farce lol
Me: exactly and that's why we need to study how can voting be not a farce
First-past-the-post gets a hard time, and deservedly so. But the people who say "first-past-the-post bad, ranked choice good" are oversimplifying. It turns out there are all these mathematical trade-offs, and it is formally provable that there is no perfect system.
Most ranked choice voting systems* can suffer from a crazy effect where getting more votes makes you lose. The technical name for this is a monotonicity failure because mathematicians are shit with names. (*There are theoretical ranked-choice votings that don't fail monotonicity, but I don't know of any being applied in a political system. Companies probably have used them.)
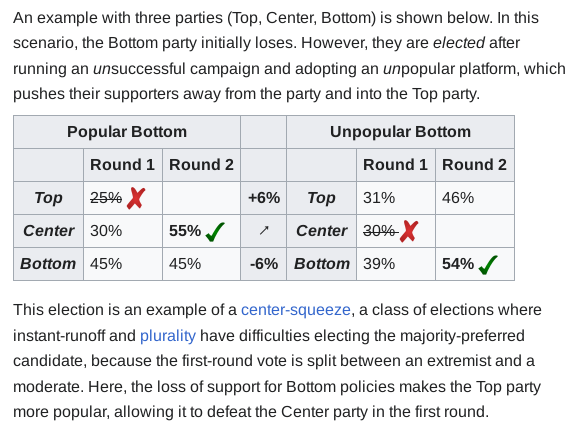
In the 'Popular Bottom' Scenario, ![]() gets 45% of the vote and isn't elected; but in the other scenario he gets 39% and is elected. What happened is he lost supporters to a rival (Top) who eliminated his other rival (Center) for him, so he was able to sneak in.
gets 45% of the vote and isn't elected; but in the other scenario he gets 39% and is elected. What happened is he lost supporters to a rival (Top) who eliminated his other rival (Center) for him, so he was able to sneak in.
First-past-the-post doesn't have this problem: more votes is always better. But it has plenty of other problems. The USA system fails the no favorite betrayal criterion catastrophically; that's the criterion that you should be able to vote for who you like best. Usans "have to" vote for a candidate they hate.
This page summarises it pretty well: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comparison_of_voting_rules with tables comparing the different traps multi-winner systems fall into and the traps single-winner systems fall into.
Some cool systems:
-
PDF – "This paper discusses the protocol used for electing the Doge of Venice between 1268 and the end of the Republic in 1797"
Anyway, interesting stuff to think about if we design democratic/anarchistic systems for collective decision-making. It wouldn't have to be electing representatives, it could be voting on policies, same maths either way.

I do think these weird elaborate examples of a city choosing where to build a hospital (or see above for the Mars colony thing) are a huuuuge red herring. Determining where to build a hospital and all other essential public infrastructure is not a question of democratic political will. The political will demands to make the hospital high quality, free at the point of access, etc. But optimization of those systems are best carried out by city planners coordinating with public transport access etc in collaboration with and overseen by citizen councils. Perhaps on a rare occasion, there really are two equally good choices, but I find that to be very unlikely most of the time with regards to these kinds of hypotheticals.
TLDR: Planning is good and can and will solve a lot of these problems. Democratic will is best imposed as oversight over a scientific planning process and through the setting of social goals. Direct policy votes probably will be appropriate in some circumstances, but I think what exactly will be learned during socialist construction.
What do you mean when you say siting a hospital is "weird eleaborate"? I picked it because it's the most down-to-earth example I could think of, it affects people's lives and deaths and is an issue I have spent hundreds of hours campaigning on.
I agree it "is not a question of democratic political will" in non-democratic societies like the USA or China. But in a society ruled by the people, then the people decide.
There's no ideological workaround for to the fact that society has to make choices. First, we need hospitals. Second, the hospitals need to be located somewhere. Third, the choice has to be made, the hospital won't be sited without some chooser. Fourth, in a people-ruled system, we need some way of converting diffuse individual wishes into a decision.
Towards a New Socialism talks about the intersection of planning and democratic choice. They say planning can produce multiple feasible plans and then the people choose among them.
TANS is exactly what I was thinking of. I'll take another look at what he recommends direct democracy for.
And regarding the hospital example... I think in many well-planned cities there is probably going to be an ideal location near the primary public transportation hub to put something as important as that. If there are two large but disparate population centers in one city, then hopefully the democratic will says build two hospitals, not one shitty one in the middle away from both population centers or simply the one in either center that gets the most votes. Of course I agree choices will need to be made, I'm just interested in balancing these choices with optimal planning. So, if something is better than RCV that's great, but I remain unconvinced that RCV isn't already a good enough improvement to immediately jump all FPTP systems to in the interim.