Apologies for posting.
I should say by way of introductory remarks, that while this is an effort post, it is an effort post on a shitposting website, and thus ab initio a shitpost and therefore be taken in the correct spirit of levity in which it is intended. Don't get my thread locked.
Recent discussion on here has touched on the moral status of the execution of the Romanov family by Bolsheviks ahead of the advancing White Army1. While not exactly of practical significance given how few of us have Royal Families locked up in our basement, it did reveal several significant, (sometimes severe) differences in the philosophical underpinnings of the posters on this website.
A Moral Communism
Moral status as such actually has very little to deal with communism/leftist (in the Marxian vein) in terms of it's internal mechanism. Marx, Engels, Lenin, and the rest of that intellectual lineage2. famously thought very little of moral philosophy. A communist is thus entirely at liberty to dismiss this entire discussion as idealism, and observe that within a Marxist framework, there are no 'good' and 'bad', merely a historically deterministic sequence of class antagonisms that will eventually resolve in favor of the proletariat and thus choosing to be a communist is merely choosing to throw one's hat in with the predetermined victors. This strand of amoral communism thus is not terribly interested in this discussion, and anyone here that adheres to that framework is excused from the discussion as having won the argument.
Given the rest of us do have moral considerations that prefigure our political beliefs, it's necessary for us to sketch out at least a scaffolding for what moral commonalities leftists share before going further, lest we fall into a morass of fundamentally incompatible frameworks stemming from different axiomatic premises. Speaking from my own personal position, I ascribe to leftist political positions as they offer me the greatest promise of granting a comfortable and dignified existence to the largest number of people possible. That in of itself does not make a moral axiom though, as achieving a large amount of something is valueless if the individual components don't themselves have value, and therefore, and a fundamental value informing my politics is the axiomatic value/sanctity of human life. So I am taking on as an assumption that generally speaking, want everyone to have dignified and comfortable lives3. If that position doesn't more or less describe you, you are also excused as having won the argument.
Justifying Shooting a Tsesarevich in my Pajamas
Which brings us to the Romanovs. In keeping with 3. above, and considering the minor children of royals not culpable for the systematic injustices perpetrated under the dictatorship of their parents, we'll limit our discussion here to the minors (Anastasia, and especially Alexei), though I think the general outline of the argument can be applied to pretty much all of the Tsar's issue. The entirety of the family, along with their retinue, were bulleted and bayoneted in Yekaterinburg about 10 days before white occupied the city. In attempting to defend the legacy of one of the most politically successful socialist projects in history4., this action has largely been justified on the left. Examining the commonly proposed justifications in light of our moral principles finds them universally lacking.
- It was necessary in order to safeguard the immediate success of the revolution against an individual with claim to the throne.
This argument goes that while we do value human life and dignity, our efforts to maximize these will sometimes require that certain human lives be forfeit, essentially turning this into a trolley problem5.. This argument differs in an important aspect from the trolley problem in that the trolley problem consists of single moment in time with clearly articulable and certain outcomes given at the outset. Leaving Alexei alive was in no way certain to doom the revolution to failure of significant struggle, as he could have been maintained in custody, and ascribing such outsized influence on the course of political affairs to the life of a sickly 13 year old is a profoundly anti-materialist approach to history. History is replete with challenges to establish socialist authority6., none of which stemmed from claimants to the Imperial thrown. Further, liquidating the Tsar, his children, and his brother did not exhaust the Romanov line, his cousin could and did proclaim himself Emperor-in-exile, and despite being old enough to actually head a restorationist intervention, none materialized. So the notion that killing Alexei was necessary fails to stand up to scrutiny 7.. It is also worth noting as an aside that the Romanovs were deeply unpopular, and to wit, were not the government the Bolshevik revolution occurred under, and supporters of the provisional government (domestic and international alike) formed the overwhelming contingent of the White forces, and the notion that a 14 year old tsarist claimant to the thrown would have had a meaningful impact on that colossal clusterfuck strains credulity.
- It prevented a longterm challenge to Boshevik control in a manner similar to Jacobite uprisings or the Bourbon Restoration.
Taking a more longterm view of the problem, it might be acknowledged that the Alexei presented no immediate threat justifying his liquidation, but, drawing from the history of pre-CIA regime changes, he presented a longterm likely/probable/plausible/possible threat in the form of an eventual challenge, and that acting in light of that possibility was justified if not strictly necessary. If we wish to examine this in light of our moral principles, we need to develop some notion of probability calculus; at what point is taking in innocent life now justified in order to avoid certain possible harms that have a certain probability of occurring. You can formalize this to ridiculous extents8., or you can take the legal systems more qualitative approach, of establish some standard of proof (you are, after all, justifying killing someone), where the execution is deemed justified if seems more likely than not/clearly and convincingly/beyond a reasonable doubt that it will prevent further, greater harm in the future. This lets you weaken the requirement that it is necessary to kill him to merely it is prudent to kill him. What is lacking though is any evidence that anyone has meaningfully carried out this process for any standard beyond plausible. The greatest extent to which this is established is that historically, there have been several restorationist insurrections, but no systematized historical study has been undertaken to quantify the risk of insurrection/coup in the presence or absence of an legitimate claimant.9.
Well perhaps we leave it there; a plausible narrative that places Alexei as the cause of some harm is sufficient in our eyes to justify his liquidation. The problem with this is that it is such a liberal standard that it can be applied to nearly everyone. There are scores of documented peasant rebellions throughout history, so by the same standard it is plausible that any given peasant may be at risk for launching a peasant rebellion down the line and thus, by that same standard, we are justified in liquidating them. Universalizing from this generic peasant^.10. to all peasants. And thus our system named aimed an providing dignity and comfort is able to justify pretty much any atrocity.
- The moral culpability of for the executions lies at the feet of the Tsar who created the system and not the executioners themselves.
This argument goes that it was actually the Tsar that placed him in position to be killed by standing at the top of a monarchical system that has ruined and ended untold numbers of lives. Had the Tsar dismantled that system before it came to blows, Alexei would have lived a happily inbred life as a continental European curiosity.
This argument plays fast an lose with the notion of fault to an extent that borders on the absurd. Within getting into the morass that encompasses the legal notion of fault, I'll observe that the executioners where in total control of the situation, given the Romanovs were in the zone of immediate material influence, while the Bolshevik leaderships were at a more distant proximity, and Tsar Nicholas II at the head of the Imperial State was a fleeting memory, having greatly influenced the events that now overtook them, but having no control over them. The Bolshevik's in Ipatiev House or those in leadership in Moscow alone decided who in that house lived and died, they knew that, and they exercised that choice.
- Unpleasant things happen during a revolution and we accept that as soon as they begin.
This is true, but once again, it comes down to the notions of control and proximity. As a leftist, I acknowledge that the struggle for political power may involve the world becoming a worse place (as judged according to my moral principles outline above) due to my actions to make it a better one. This is an abstract acknowledgement. It may also result in me taking actions that I find unpleasant or repugnant11. If it is the moral principles that describe motivate my political struggle though, it is fundamentally self-defeating to exercise my control over my immediate surroundings to knowingly act in a manner that results in an immediate degradation of the world around me (once again, as judged by my moral standards). My actions in the here and now, must be justified according to my principles in the here and now and my actions in the here and now. If 10 minutes ago I was standing in Yekaterinburg and the Whites are closing in, and now I'm still standing in Yekaterinburg and the Whites are still closing in, but now there is a brand new pile of child corpses of my making, then I have made the world a worse place.
No tears for dead peasants
It is reasonable to ask why go to such great lengths to challenge the justifications for the murder of Alexei (which is so emotionally remote to me as to essentially be fictitious). To which I offer the following justifications.
- It's ridiculous and therefore funny.
- Because eventually some of us may be in positions to make decisions that make the world a substantially better or worse place for others, and I want it be very clear what stands before us when making those decisions. No, none of us are going to decide whether or not an heir lives or dies, but we are going to decide how to treat with those around us, and want everyone to pause before they exercise what little control they have in the world around them before making it a worse place, justifying it with a glib aphorism or some half-baked argument.
1. The fitness for humor here is not considered, as something can be both morally bad and the legitimate target of well-done comedy. Like 9/11.
2. I was promised ice cream if I didn't say 'ilk' here.
3. To wit, one of the main justifications for political violence on the left is that it is directed at those preventing others from enjoying dignity, comfort, or well, life.
4. Such as it is.
5. which we may dub the Yekaterinburg Streetcar Defense
6. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Rebellions_in_the_Soviet_Union
7. One could alternatively take the logical form of necessity as a conditional, ~P -> ~Q with P being "the legitimate claimant to the imperial thrown is killed" and "Q" being "the revolution is successful". Given the contra-factual nature of ~P, the truth value of this statement can't be evaluated directly, but given the analogous situation in China with PuYi, we can strongly infer that this conditional is in fact false and thus logical necessity is not present.
8. define xi to be each enumerated possible future in space X, p(xi) to be the probability of that future occurring, and h(xi) to be the number of lives ruined by Alexei in that future xi. Shoot kid if
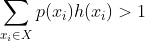
9. To reach a preponderance of evidence standard you would need to establish P(Insurrection|Legitimate Claimant) > P(Insurrection), which the strictly materialist interpretation would hold P(Insurrection|Legitimate Claimant) = P(Insurrection).
10 Regular viewers will recognize this as universal generalization.
11 Orwell's description of the conditions of fighting in the Spanish civil war come to mind.


This folds under scrutiny. Any given peasant may pose a threat of revolt, but a royal heir poses a specific threat, and of a much greater magnitude in both likelihood and severity that the two cases are not comparable. There existed specific powerful groups who had a vested interest in putting an heir to the throne back onto it, and the means to attempt to do so in bloody fashion.
In this case, the specific qualities of the subject set them apart from the general population. I liken it to BRCA positivity. Yes, any given breast may cause cancer. However, it is not prudent to excuse every breast. It is prudent to excise one's breasts if one is double BRCA positive. One does not have to do this, but it is a reasonable response to a specific threat that can prevent greater harm in the future.
I make specific reference to the fact that no one has shown their workings when making the claim that the likelihood of a revolt is higher in the presence of an heir or that the likelihood of a revolt being led by a nonheir is less than the likelihood of a revolt being led by an heir. BRCA positivity has a great deal of work behind it specifically quantifying the probabilities in question.
This interest and possibility existed independent of Alexei. There was an entire extended Romanov tree to contend with, and there still in fact is. Not to mention the fact that there was no shortage of fake Romance running about whose cause they could appropriate.
The specific mechanism driving the elevated risk associated with an heir is hereditary monarchy. While I cannot produce a scholarly work examining the lineages, both actual and claimed, of the individuals advanced by rebel factions throughout, say, Eurasia from 1400-1900, I would assert that a cursory study confirms that individuals perceived to be legal heirs under the laws of their given title (and who subsequently are denied that throne) have a significantly higher correlation with driving civil war than those not holding such a position. The child and heir of the latest monarch, while not the only claimant who could be co-opted by a faction, is certainly one which would command the most legitimacy to the nation at that time.
Were there Romanovs in a similarly vulnerable position that were spared intentionally, or were these individuals unreachable by the same forces that determined the risks of leaving the proximal Romanovs posed sufficient threat to be eliminated?
It's doubtful to me that one could ever justify, with formal logic, that the Romanovs' deaths were necessary, but their killing was rooted soundly in an understanding of the propensity for monarchs and all who associate with them to engage in violence to preserve, even if not the rule of specific monarchs, the institution itself.
But the whole point in discussing a justification is in actually filling in the details. If you want to claim that the murders were justified on the basis of some probability, you have to justify where you arrived at that probability, not where one could arrive at a suitable probability and handwaving away the difficult work.
Does it matter? If the claim is that killing the entire issue of the Tsar is needed to avoid the possibility of a royalist, you have to show that it in fact does so, and the fact that the royal line passes to someone outside of their custody, and of age on the killing of the tsars famility would seem to actually increase that threat as opposed to reduce it.
They are certainly rooted sounded in that assumption, but there's no evidence that the bolsheviks or anyone else engaged in formalizing this notion of a propensity beyond gesturing at it.
Any good study should acknowledge its limitations. In this case, applying statistical analysis to historical events faces the issue that statistical analysis is highly dependent on data integrity and on the ability of future events to be predicted by historical data. When we are discussing a proletarian revolution and attempting to predict how the forces of reaction will attempt to combat it, we lack a representative sample in 1918. In this case, we must take the approach of the clinician rather than the pure theorist. Statistical analysis is an invaluable data point, but it is a data point among others. Understanding of the underlying mechanism can and ought to drive decision making in the absence of conclusive data.
Does it matter that they can't kill Romanovs they don't have in custody? Yeah, I'd argue that that puts a damper on things. "There's Romanovs now" obscures a lot of information about where they are at that time and whether they were even in a position to be executed. Additionally, the entire issue of the dynasty need not be exterminated if the most likely threat is that his direct male-line heir is used as a tool by counter-revolutionary forces. The previous Tsar's child will enjoy broader support than a cousin by virtue of proximity.
Getting back to my core problem with this argument, "why not just kill everyone" is a poor component of an otherwise well documented and well thought-out post. I think you make some thought provoking points and genuinely care about the moral calculus of revolution.
This limitation extends to any methodology we attempt to use to justify shooting Alexei based on the consequences, and fatally so.
To put my point more clearly. On the death of the tsar, to legitmate (hah) claimant to the imperial Russian throne was.
On shooting him, it was Grand Duke Kirill Vladimirovich
If you were a royalist looking for a return to the tsarist system, which of those would be a more attractive option to rally behind? From a clinical perspective, it would the greater risk would be an iatrogenic uprising.
And yet monarchists feuded amongst themselves until 1929 over the rightful heir. I have a low level of confidence that this would be the case with a surviving Alexei.
You know this in large part stems from the lack of knowledge over who whether or not Alexei and others were in fact alive. Ambiguity that couldbe maintained whether or not he is in fact dead.
Can you demonstrate that, had their deaths been confirmed, removing the ambiguity, there would not have been competing claims to the throne? It is a sound line of argument that removing the most legitimate heir to the throne would necessitate that monarchists either arrive at an agreement on a suitable substitute or else settle their differences, consuming their time and energy.
You instead seem to be making the case that he could have been kept alive, but with rumors of his death disseminated. How long could such a situation really have persisted? Everything leaks, and faster than expected. If there was a prince locked away, who is providing for their needs of life? What do the locals say about that location? It's difficult to accept the claim that a live prince publicly declared ambiguously living is equivalent in its effects to a dead prince not confirmed dead.
Historically, indefinitely.
I don't understand this notion of 'most legitimate heir' that keeps cropping up in a feudal system with a clearly delineated system of patrilineal succession. There is a single legitimate claimant via that system, and everyone else is a nonlegitimate claimant. The only confusion stemmed from the fact that no one knew conclusively who was alive. The Grand Duke was the sole, exclusively, equally legitimate claimant, in the same way Alexei would have been. But in fact only the Grand Duke was in position to push that claim.
A case remarkable for its singular, improbable nature makes a poor argument for calculated policy.
Then pick a different name for it, "person whose claim to the throne could mobilize the most rubles, guns, and hands to hold them". Non-legitimate claimants may still gain the throne by force of arms motivated by virtue of their adjacency to the last legitimate holder of power. The law exists, but its ability to influence action and the ways it will be rhetorically implemented are not cut and dry. Legally, Peter I was a non-legitimate Tsar while Ivan V should have ruled alone, but de jure legitimacy and "that quality which will motivate believers in a feudal monarchy to support a candidate materially" are not one and the same. "Being the child of the last guy" is a rhetorically resonant plank for such a believer.
Well, a lot of the other cases like the princes in the tower were ambiguous and remain so, so...?
Like clearly in this case it's the 42 year old veteran who is not under Bolshevik custody as opposed to the 13 year old sickly hemophiliac who is in Bolshevik custody right?
Has convinced me to disengage. Have a good night.
I mean that it's a bit due to it's 'angel dancing on the head of a pin' nature, not that I'm arguing in bad faith, but in any case, I appreciate you being one of the few people (the other's being @AssortedBiscuits@hexbear.net and @Zuzak@hexbear.net ) to engage with the question more deeply as opposed to just saying "read a history book" like that actually justifies anything.
Cheers
(I will comment here since I got a nice shoutout and this comment will be based on your previous replies to me and to other people)
I think the fundamental disagreement is over the nature of line of succession.
Your conception is very procedural based. It's essentially an unambiguous list where everyone's place is clearly defined and can go on practically indefinitely, for this list through each English male descendant who isn't Catholic(?). Under this conception, then yes, killing Alexei would be terrible because you're basically killing a disabled 13 year old boy only for the yellow icon to move to the next bozo. And killing that bozo would do nothing since the yellow icon would move to the next bozo and so on. If anything, killing him would be bad since instead of having a 13 year old puppet who is over his head be a rally point for reactionaries, you would have some shitty grand duke or admiral instead, an adult who can actually be a conscious agent for reaction. Plus, there's always a chance Alexei would die anyway from a serious fall, and his death would be under the White's watch.
My conception is different. Based on how feudal lines of succession actually play out throughout history, it's far more arbitrary, vibe-based, and overall completely asspully than what a clear list would suggest. To give an example, a woman somehow became emperor of China. She had the same title as every male emperor before and after her, reigning for 15 years, not bad for an emperor, certainly not bad for the only female emperor. "But how can the Son of Heaven be a woman?" Stfu peasant, now go toil in the rice fields, that's how. If you carefully study many successions, especially when a dynasty is under crisis and the heir apparent everyone likes suddenly dies and the following person next in line is someone nobody likes, there's so much bending of the rules and arbitrary titles and exceptions that conveniently allows a particular person to cut in line, if not all-out dynastic warfare. People can cut in line because the line is ambiguous after a certain point. Who is closer in line of succession, the late king's cousin or the late king's third son? Well, the cousin has the entire aristocracy and ministries on his side while the third son is only 3 years old. This also means that not all positions within that list are equal, so people who would die for the sake of the healthy and virile heir apparent won't do shit for some random third cousin twice removed dude who's also infertile and looks kinda ugly.
The million dollar question is which side does a 20th century eastern European absolute monarchy belong to, the procedural side where line of succession is completely unambiguous and automatic or the asspully side where everything is more or less completely made up and done through feudal vibes? Or I guess more accurately, were their executioners justified in thinking the Russian Tsardom has an asspully line of succession and killed the immediate imperial family with the hope that the surviving claimants would eventually fight with each other due to how ambiguous the line of succession actually is in practice?
I would disagree with your latter point. Nobody is arguing that Alexei himself would be leading an army, but that he would be used as a rallying symbol for such an army. In all likelihood, the Grand Duke would be leading a military charge either way—the question is whether it is preferable he does so with or without the legitimacy of office that a direct male heir represents under the feudal system.