spoiler
An invasive species capable of wiping out entire aquatic ecosystems and causing millions of dollars in damage to infrastructure has been found for the first time in the Colorado River, the most important river in the American Southwest.
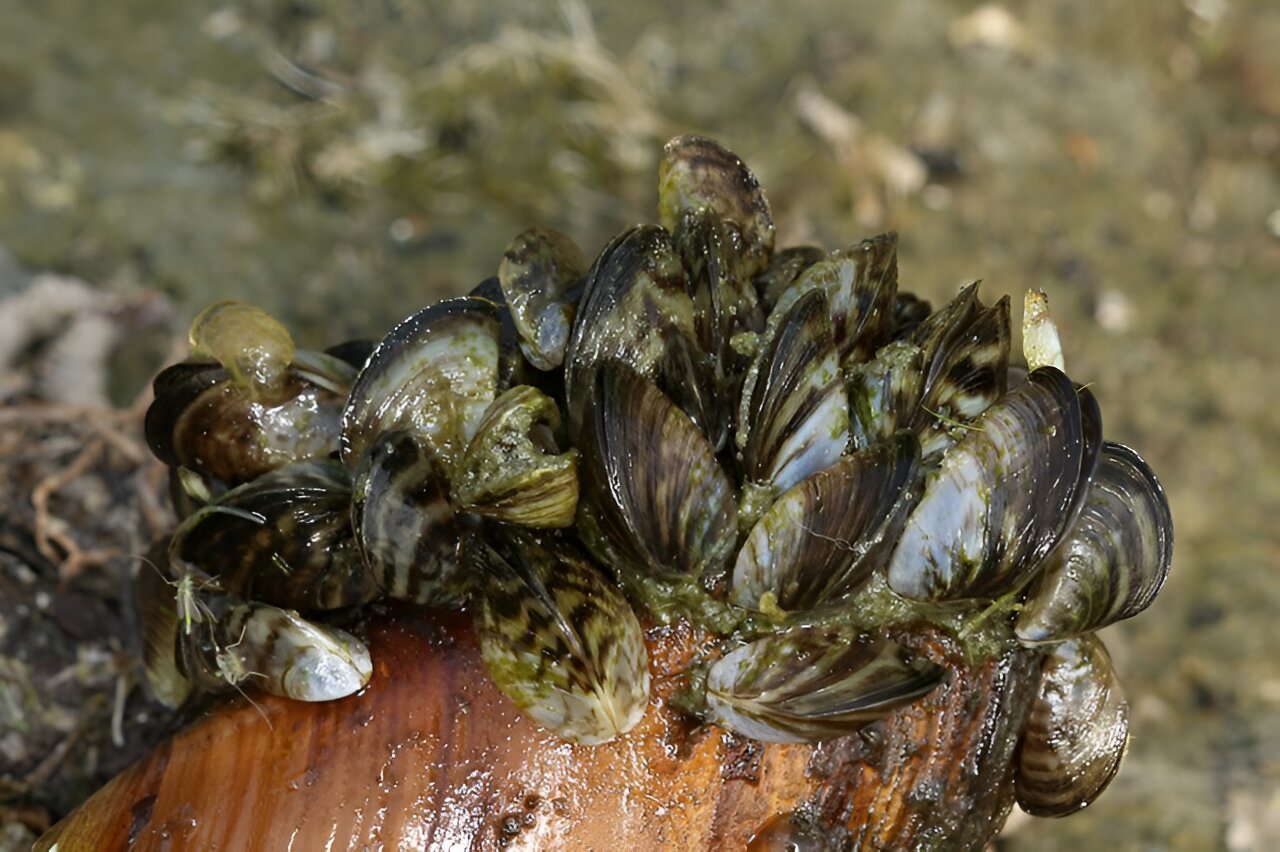
Colorado Parks and Wildlife officials on July 16 announced the discovery of zebra mussel larvae in the river east of Grand Junction. The mussels are nearly impossible to remove and pose an extreme risk to the critical river, its wildlife and its infrastructure, experts and state officials said.
The discovery of the mussels so far upstream on the 1,450-mile river means the species could easily spread downstream and take over large swaths of the Colorado, said Reuben Keller, a professor who studies aquatic invasive species in the School of Environmental Sustainability at Loyola University Chicago. There is no effective way to remove the mussels from a river once they are established, he said.
"Zebra mussels getting into the Colorado River is the beginnings of what could be an enormously damaging and widespread infestation," Keller said.
The Colorado River, known as the lifeblood of the Southwest, flows from headwaters in Rocky Mountain National Park to the Gulf of California in Mexico and makes modern life in the region possible. The river and its major tributaries provide drinking water and power for 40 million people, irrigate millions of acres that feed the country and provide crucial habitat for thousands of species.
Native to eastern Europe, zebra mussels obliterate ecosystems by eradicating basic food sources other species rely on. The small mussels attach to hard surfaces, like rocks, and grow in thick mats that kill plants and prevent insect life. The mussels feed on algae and stip all of it out of the water, eliminating the base of the food chain in many aquatic ecosystems. Food sources are destroyed for species that rely on aquatic vegetation, insects or algae—which is all species.
No species in the western U.S. has evolved to eat the mussels, Keller said, at least not reliably.
"They just take over all of that habitat," Keller said. "Ecologically, that's obviously problematic."
Colorado Parks and Wildlife found the first zebra mussel larva—called a veliger— on July 1 during routine testing in the Government Highline Canal, which is diverted from the Colorado River just east of Grand Junction. On July 8, CPW staff collected samples from two locations upstream of the canal diversion. They found a single veliger in each sample.
CPW staff have not yet found adult mussels, but they plan to conduct increased sampling. Slower sections of water, like pools and eddies, are more susceptible to mussel infestation, according to the agency.
Anyone who uses the river or surrounding waters needs to clean, drain and dry any watercraft or equipment, CPW spokesman Rachael Gonzales said.
"We're looking at what's next," she said. "It's going to be very difficult—if not impossible—to remove and eradicate them in a system as large and complex as the Colorado River."
While the zebra mussel is new to the river, the closely related and equally pernicious quagga mussel has established a population further downstream. Large infestations have taken root in the system's largest reservoirs—Lake Mead and Lake Powell—and caused millions of dollars in damage to dam infrastructure.
Zebra mussel veligers can be seen only with a microscope and float freely in river water. They are hardy and can travel miles before attaching to a surface, Keller said. A single female mussel can release up to a million veligers a year, he said.
The mussels multiply rapidly once they are connected to a surface and can clog pipes, drains, pumps and other water infrastructure, leading to costly and difficult repairs. When they die, their shells can obstruct motors and other moving parts of dams, boats and other machinery.
The Government Highline Canal, where the first larva was found, provides irrigation water to more than 23,000 acres of farmland in the Grand Valley. The canal, operated by the Grand Valley Water Users Association, is 55 miles long and sends water down 150 miles of pipes and irrigation systems.
"This news is devastating," Tina Bergonzini, general manager of the Grand Valley Water Users Association, said in a news release. "Having our canal and the Colorado River test positive increases the threat of this invasive species and could impact everyone in the Grand Valley. From irrigation to drinking water, the ramifications cannot be underestimated or overstated."
Bergonzini said the association will join CPW and federal officials in stepping up its efforts "to protect our infrastructure, the livelihoods of so many and water security for us all."
Biologists first discovered zebra mussels in the U.S. in 1988 in the Great Lakes region. Since then, they have spread via waterways and human transport across a huge swath of the eastern half of the country.
Larvae can spread into a new waterway by attaching to boats, boots or any other submerged objects, and then unwittingly be released later if those objects are not sufficiently cleaned.
Federal and state agencies for decades have fought to keep the mussels from spreading into the West. Data from the U.S. Geological Survey shows that since 2007, the mussels have been detected in three Western states: California, Colorado and Utah. The species failed to establish itself in Utah but survived in California.
In Colorado, the species did not take hold in Grand Lake and Pueblo Reservoir but has been established in Highline Lake at Highline State Park, northwest of Grand Junction.
CPW first found the mussels in Highline Lake in 2022 and launched a multiyear, multistep process to kill the species and stop the spread. That winter the agency lowered the lake's water level by 30 feet to freeze the mussels and then applied a copper solution to kill them.
But the mussels were found again in October 2023, and CPW planned to drain the lake to kill the mollusks.
It's possible the mussels aren't faring well in the Colorado River and the detected veligers will not establish a population, said Keller, the Loyola professor. But that scenario is highly unlikely, especially with the robust population of the quagga mussels further downstream.
"I wouldn't hold out too much hope that the species won't take off," he said.
Shit. This fuckers have decimated life in the great lakes. They are hardy filter feeders that multiply like crazy. I've seen them over the years take out the bottom of the food chain. Seeing the lake go from all kinds of different plankton to hardly any variety. This has a direct effect on the fish population all the way to the top.
One of the neatest civil engineering projects I've seen is the Big Thompson Project: https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Colorado%E2%80%93Big_Thompson_Project
80% of Colorado's water is on the west side and 80% of its population is on the east side. We use an elaborate series of canals, pipes, and reservoirs to make Denver and our big agricultural areas possible. If that gets clogged up, it's going to be devastating to a huge chunk of the state which is already straining to find enough water. That kind of overdevelopment needs to die but those agricultural areas are our most reactionary so it could be a messy death.
hydrology and the modern hydrologic city is something that I slept on until I was in a geography and natural resources class, and the instructor had us watch a documentary about water.
in 100 A.D Rome had a population of reportedly 1,000,000. this was at its peak of development and the most sophisticated hydrologic city in the west, drawing fresh flowing water via maintained aqueducts from distant places. places all over the city had a constant outflow of fresh flowing water for unlimited gathering by people, not to mention the bath and steam houses.
when the austerity trap and institutional rot came over the next centuries, one of the first public works projects to fall away were the "expensive" aqueduct maintenance and development projects. as the volume of water flowing into Rome collapsed, so did it's population. by ~550 AD, Rome's population was somewhere between 30-100K where it would stay for more than a thousand years.
often, historical accounts blame it on conflict, disease and out-migration. after all, what is left of life when there isn't sufficient clean water to go around?
i mean there is a very specific and chapters long explanation of exactly how Belisarios depopulated the city in 537, he deported everyone who wasn't a solider to conserve grain. they might've been able to return but the city was exchanged 3 more times and the plague hit. it's one of those times the basic sources are impactful enough that the systemic doesn't feel needed
but the long-durree systems that had maintained ancient cities disappeared in the entire mediterrean, not just the places with apocalyptic armed conflict. and it has a lot to do with the state budget because the army was increased in size and expense
It really is amazing how these things can thrive so far outside of their natural habitat, the inside of a zebra.
the boater kulaks can't stop talking about these things around me. the great divide among their class is whether precautions are justified/acceptable or they should just let it rip. honestly it's very similar to how the covid precautions debate played out.
oh yeah? lets see if these mussels can survive when there's no water in the colorado. big talk from an aquatic species in the most aggressively draining river in the US
spoiler
death to boaters, of course







