(Images can be enlarged if needed)
Cardiac arrest, also known as Sudden Cardiac Arrest, is when the heart stops beating suddenly. The lack of blood flow to the brain and other organs can cause a person to lose consciousness, become disabled or die if not treated immediately.
The terms ‘heart attack’ and ‘cardiac arrest’ are often used interchangeably, but these are two different heart conditions.
A heart attack occurs when there is a blockage in the arteries that stops blood flow in the heart. Due to the lack of blood and oxygen flowing in the heart, the heart muscle tissue will become damaged. Heart attacks can increase the risk for cardiac arrest because heart attacks can alter electrical signals in the heart.
CPR – or Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation – is an emergency lifesaving procedure performed when the heart stops beating. Immediate CPR can double or triple chances of survival after cardiac arrest.
If someone experiences cardiac arrest, they need immediate treatment to increase the flow of oxygen-rich blood to their organs. CPR is the compression over the chest to manually pump a patients heart. Rescue breaths are preformed to provide oxygen to the body.
During CPR, proper hand placement on the lower half of the sternum is crucial. Placing hands over the sternum ensures effective chest compressions directly above the heart, optimizing blood circulation throughout the body.
According to the American Heart Association (AHA), the overall survival rate for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest is around 10%. However, survival rates can be improved if bystander CPR is started immediately. Studies have shown that bystander CPR increases the chances of survival for someone experiencing cardiac arrest. In fact, the AHA reports that survival rates increases to 40% or higher when bystander CPR is performed promptly. The surival rate is between 24% and 40% for those that happen in the hospital, according to the report published online in the Emergency Medicine Journal.
CPR is preformed between 100 - 120 beats per minute. Famously Staying Alive by the Bee Gees is the same beat. A large list of songs with the correct BPM can be found here
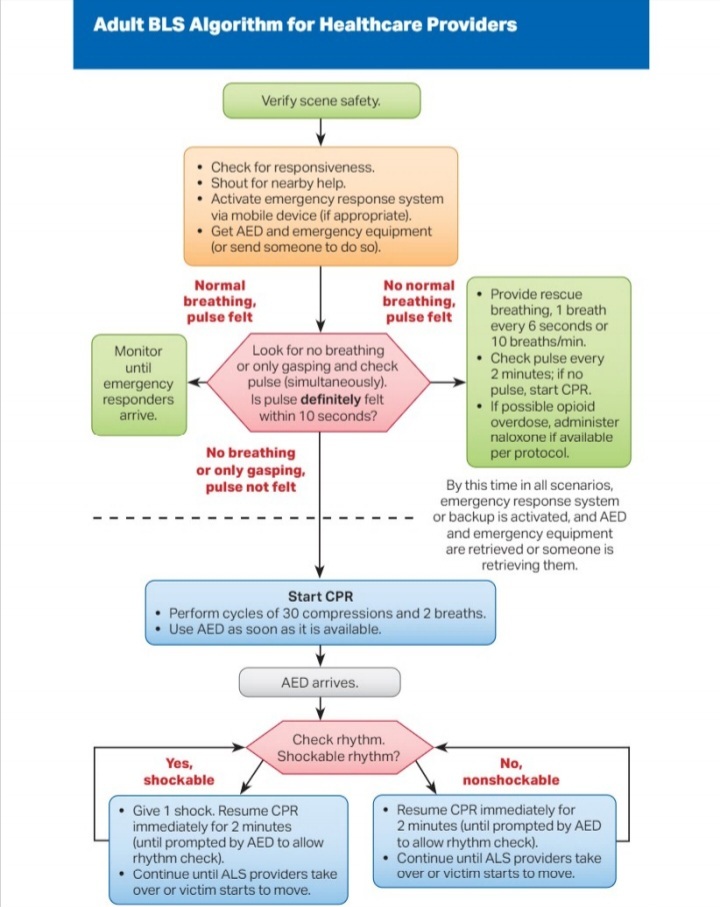
![]() The American Red Cross gives the following list of steps to asses if CPR is needed and how to preform:
The American Red Cross gives the following list of steps to asses if CPR is needed and how to preform:
1 CHECK the scene for safety, form an initial impression and use personal protective equipment (PPE)
2 If the person appears unresponsive, CHECK for responsiveness, breathing, life-threatening bleeding or other life-threatening conditions using shout-tap-shout
3 If the person does not respond and is not breathing or only gasping, CALL 9-1-1 and get equipment, or tell someone to do so
4 Kneel beside the person. Place the person on their back on a firm, flat surface
5 The American Red Cross CPR guidelines recommend 100 to 120 chest compressions per minute, 30 at a time. Remember these five points:
Hand position: Two hands centered on the chest
Body position: Shoulders directly over hands; elbows locked
Compression depth: At least 2 inches
Rate of compressions: 100 to 120 per minute
Allow chest to return to normal position after each compression
6
Give 2 breaths
Open the airway to a past-neutral position using the head-tilt/chin-lift technique Pinch the nose shut, take a normal breath, and make complete seal over the person’s mouth with your mouth. Ensure each breath lasts about 1 second and makes the chest rise; allow air to exit before giving the next breath Note: If the 1st breath does not cause the chest to rise, retilt the head and ensure a proper seal before giving the 2nd breath If the 2nd breath does not make the chest rise, an object may be blocking the airway
7 Continue giving sets of 30 chest compressions and 2 breaths. Use an AED as soon as one is available! Minimize interruptions to chest compressions to less than 10 seconds.
Sources:
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/cardiac-arrest
https://cpr.heart.org/en/resources/cpr-facts-and-stats
https://www.mycprcertificationonline.com/blog/cpr-success-rate
Instructional images from the AHS Basic Life Support Manual (2020)
Join our public Matrix server! https://matrix.to/#/#tracha:chapo.chat
As a reminder, be sure to properly give content warnings and put sensitive subjects behind proper spoiler tags. It's for the mental health of not just your comrades, but yourself as well.
Here is a screenshot of where to find the spoiler button.


It is physiologically impossible for your rate of strength gain to increase or for your absolute strength to increase, assuming you are already well trained, after dropping to adrenal levels of testosterone from gonadal levels.
So idk if this is well trained or not but I was deadlifting 315 3x5, squatting 225, and benching idk like 185 (maxed at 205 but couldn't do that regularly) at about 145 pounds. I'm 155 pounds and doing similar, but it's easier on the deadlift, I think I hit maybe 325 or 335 like 3 months ago. I did 300 and it was pretty damn easy yesterday, I could push it further. I could have honestly been under training though because deadlifts that heavy kinda scared me, form would start to break down and I worried about injury
With those lifts at that bodyweight, you are trained enough to be considered an intermediate lifter. The fact that you haven't noticed any drop off in strength, in contrast, actually seeing your progress continue to climb, 10 months after you (hypothetically) took your testosterone levels to adrenal levels from gonadal levels is literally not how the human body works idk what to tell you. The effects of androgens on strength and body composition is very clear cut and well studied, you don't just "get stronger" after starting feminizing HRT unless it isn't suppressing your androgen production, or you didn't produce normal gonadal levels of androgens in the first place, or you are a novice lifter (which you don't appear to be from those lifts but idk).
Idk what to say really about this, I am gonna get my levels checked this week or next week I'll tell you what's up haha. My T levels were at around 800 before I transitioned
That's never a bad idea, if it turns out your levels are adequately supressed, my only other guess is that you just have unusually low levels of androgens receptors in you muscles, which would mean your muscles did not receive as much androgenic signaling as they normally would with those higher levels of serum testosterone. That, or you were just really strong to begin with and those lifts were close to your untrained numbers?
Maybe honestly it's the last part idk. I'm quite muscular and I at least used to build muscle pretty easily
Just got my levels back - testosterone is 25 and estrogen is 233 at trough
I will say though I don't get random erections anymore. I haven't gotten random erections since like idk my T was around 100
What is "well trained" I guess? I also never stopped training? Idk what to say I'm just happy my strength is still around for the most part. It feels like in some ways I have gotten stronger but maybe I should go test my maxes??